Orthopedic procedures play a vital role in restoring and maintaining musculoskeletal health. From addressing fractures to treating chronic conditions like arthritis, these procedures encompass a broad spectrum of interventions aimed at improving mobility, reducing pain, and enhancing overall quality of life. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the intricacies of orthopedic procedures, from diagnosis to recovery, highlighting the latest advancements and patient success stories along the way.
Introduction to Orthopedic Procedures
Orthopedic procedures encompass a diverse range of medical interventions focused on the diagnosis, treatment, and rehabilitation of musculoskeletal conditions. These conditions may affect bones, joints, ligaments, tendons, muscles, or nerves, often resulting in pain, limited mobility, and decreased functionality. The field of orthopedics is dedicated to addressing these issues through both surgical and non-surgical means, with the overarching goal of restoring optimal musculoskeletal health.
Common Orthopedic Conditions
Arthritis
Arthritis, characterized by inflammation of one or more joints, is a prevalent orthopedic condition affecting millions of people worldwide. The most common types include osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, and psoriatic arthritis, each presenting unique challenges and treatment approaches.
Fractures
Fractures, or broken bones, can occur as a result of trauma, repetitive stress, or underlying medical conditions. Orthopedic procedures for fractures may involve realigning the bone fragments through casting, splinting, or surgical intervention, depending on the severity and location of the fracture.
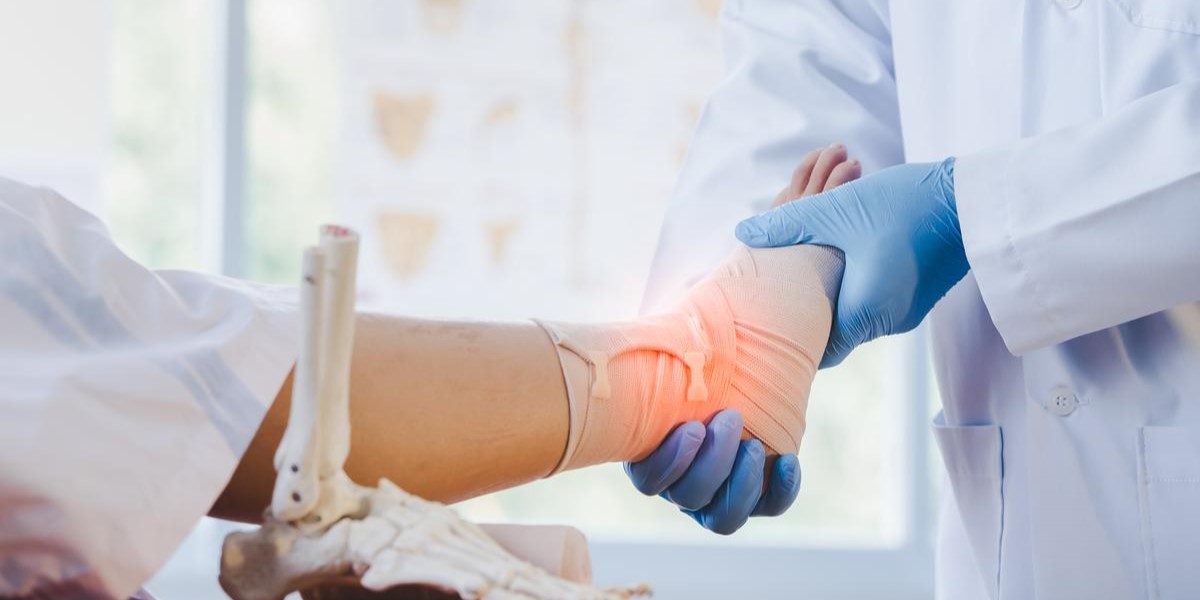
Tendon Injuries
Tendons are fibrous tissues that connect muscles to bones, facilitating movement and stability. Injuries to tendons, such as tears or ruptures, can occur due to sudden trauma or overuse. Orthopedic procedures for tendon injuries may include surgical repair or reconstruction to restore function and prevent long-term disability.
Ligament Injuries
Ligaments are tough bands of tissue that connect bones to each other, providing stability to joints. Injuries to ligaments, such as sprains or tears, are common, particularly in weight-bearing joints like the knees and ankles. Orthopedic procedures for ligament injuries may involve surgical reconstruction to restore joint stability and prevent recurrent instability.
Diagnostic Techniques
Accurate diagnosis is paramount in guiding orthopedic treatment decisions. Various imaging modalities and diagnostic tests are utilized to assess the extent of musculoskeletal injuries and conditions, including:
- X-rays: These provide detailed images of bones and can help identify fractures, arthritis, and other bony abnormalities.
- MRI Scans: Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) offers high-resolution images of soft tissues, including muscles, tendons, ligaments, and cartilage, aiding in the diagnosis of injuries and conditions such as ligament tears and cartilage damage.
- CT Scans: Computed tomography (CT) scans produce cross-sectional images of bones and can detect fractures, bone tumors, and complex bony abnormalities with greater detail than traditional X-rays.
- Ultrasound: Ultrasonography is used to visualize soft tissues and can be particularly useful in diagnosing tendon and muscle injuries, as well as assessing joint inflammation and fluid accumulation.
Non-Surgical Treatments
Many orthopedic conditions can be effectively managed with non-surgical interventions, tailored to the individual needs and preferences of the patient. These may include:
- Physical Therapy: A cornerstone of conservative orthopedic management, physical therapy aims to improve strength, flexibility, and range of motion through targeted exercises, manual therapy techniques, and functional training.
- Medications: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), analgesics, and corticosteroids may be prescribed to alleviate pain, reduce inflammation, and improve function in conditions such as arthritis and tendonitis.
- Injections: Corticosteroid injections, hyaluronic acid injections, and platelet-rich plasma (PRP) injections may be administered directly into affected joints or soft tissues to provide targeted pain relief and promote tissue healing.
Surgical Options
When conservative treatments fail to provide adequate relief or when musculoskeletal injuries are severe or complex, surgical intervention may be necessary. Orthopedic surgery encompasses a wide range of procedures, including:
- Arthroscopy: A minimally invasive surgical technique that involves inserting a small camera (arthroscope) and specialized instruments through small incisions to diagnose and treat joint problems such as torn cartilage, loose bodies, and damaged ligaments.
- Joint Replacement: Total joint replacement surgery, such as hip replacement or knee replacement, is performed to remove damaged or diseased joint surfaces and replace them with artificial implants made of metal, plastic, or ceramic materials.
- Fracture Fixation: Surgical fixation of fractures may involve the use of metal screws, plates, rods, or external fixation devices to stabilize fractured bones and promote healing.
- Soft Tissue Repair: Procedures such as tendon repair, ligament reconstruction, and rotator cuff repair aim to restore the integrity and function of damaged soft tissues, often using sutures, anchors, or grafts to facilitate healing.
